
In humans in tendons, the walls of blood vessels, cartilage, bone, gumsĬollagen is strong but still flexible – this is important in tendons which cannot be rigidĪ repeat sequence of 3 amino acids glycine-proline-X (any other amino acid) It is found in many diverse organisms and organs:

These chains are linked by disulphide cross bridges – making the proteins very stable and strongįibrous proteins have Structural functions: Polypeptides form long chains running parallel to each other The 3D-shape of globular proteins is critical to their function – slight changes can have radical effects – eg in sickle cell anaemia one amino acid change causes a shape change in the molecule that in turns reduces the ability of haemoglobin to bind to oxygen and changes the shape of the whole red blood cell from a biconcave disk to a sickle shape. When haemoglobin is bound to oxygen it is called oxyhaemoglobin and the colour changes from purplish red to bright red Human haemoglobin has four polypeptide chains and four haem groups and can therefore carry 4 x O 2 molecules The Hydrophilic R-groups are arranged around the outside of the molecule which allows Haemoglobin to mix with the watery medium inside red blood cellsĪttached to each polypeptide chain is a prosthetic HAEM group with an Fe2+ ionĮach Fe2+ ion can combine with one O 2 molecule The precise 3D-shape of the Haemoglobin molecule is absolutely critical to it's Oxygen-carrying function Haemoglobin has a quaternary structure made up of 4 separate polypeptide chains:Ģ identical alpha -chains with 141 amino acids eachĢ identical beta -chains with 146 amino acids eachĮach polypeptide chain is folded/coiled into a compact shape due to hydrophobic interactions between the (hydrophobic) R groupsĪll 4 polypeptide chains are linked to form a roughly spherical haemoglobin molecule

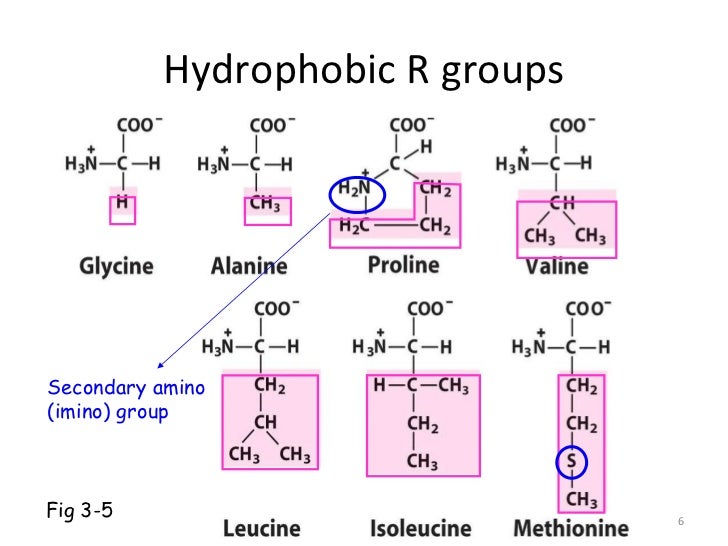
Tertiary structure refers to the overall folding of the entire polypeptide chain into a specific 3D shape. The two most common folding patterns are the alpha helix and the beta sheet. Protein secondary structure refers to regular, repeated patters of folding of the protein backbone. The primary structure is the sequence of the amino acids. Proteins are composed of 20 different kinds of amino acids joined in a linear polypeptide chain by peptide bonds. You may discover that all of the answer choices are correct!
Here is a review of features of protein structure that can be used to analyze the different answer choices. Which statement is true concerning the structure of proteins?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
